What is Email spoofing?
Email spoofing is one such a method used in spam and phishing attacks to trick users into believing that the message has come from a person or organization they trust. Hackers mostly use spoofing emails to obtain personal information, sensitive information, security numbers, financial details and other information.
The goal of email spoofing is to trick recipients into opening or responding to a message. When an email address is spoofed, the spammer does not get access to your account.
What will happen if you open a fake email?
Simply opening a phishing email will expose you to a virus or malware. Almost all viruses, such as Trojan horses or worms, become active when you download an attachment or click on a link in an email. Hackers can just detect that you have opened the email.
Client applications specify a sender address for outgoing messages so outgoing email servers cannot identify whether the sender’s address is real or spoofed.
A Brief History of Email Spoofing
Email spoofing is an invention of the 1970s because of the way email profiles work. It started with spammers trying to bypass ICS utility email filters. This outcome was further developed in the 1990s, then became a global cybersecurity requirement in the 2000s.
Security protocols were introduced in 2014 to help fight email spoofing and phishing. Since then, many fake email messages are now sent to user spamboxes or rejected and never sent to recipient inboxes.
How does email spoofing work??
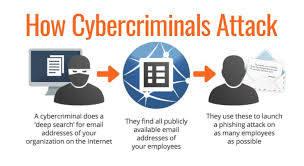
The purpose of email spoofing is to trick users into believing that the email is from someone they know or trust – in most cases, a coworker, vendor, or brand. Taking advantage of that trust, the attacker asks the recipient to reveal information or take some other action.
A common email client (such as Microsoft Outlook) automatically records the sender’s address when a user sends a new email message. But an attacker can send messages programmatically using a basic script in any language that configures the sender address to a chosen email address. The Email API endpoint allows the sender to specify the sender’s address, regardless of whether the address exists or not. And outgoing email servers cannot determine whether the sender address is valid.
There are three major components of email:
sender’s address
receiver’s address
Email body
Another component often used in phishing is the reply-to field. The sender can configure this field and use it in a phishing attack. The reply-to address tells the client email software where to send the reply, which may be different from the sender’s address. Again, the email server and SMTP protocol do not verify whether this email is legitimate or spoofed. It is up to the user to understand that the reply is going to the wrong recipient.
Examples of Email Spoofing
As an example of email spoofing, an attacker could create an email that looks like it comes from PayPal. The message tells the user that their account will be suspended if they do not click on a link, authenticate on the site, and change the account password. If the user is successfully tricked and types in the credentials, the attacker can authenticate into the targeted user’s PayPal account and steal the user’s money.
To the user, a fake email message appears legitimate because many attackers use elements of the official website to make the message appear more credible.
How to protect from email spoofing??
In addition to a savvy team monitoring suspicious emails, specific equipment and technologies can help prevent email spoofing from becoming a threat.
Secure email gateway: A secure email gateway can help protect against email spoofing by filtering suspicious messages and blocking messages from known spoofed email addresses.
Implement email authentication protocols: Implement Sender Policy Framework (SPF), domain keys, identified mail (DKIM), and domain-based message authentication, reporting, and conformance (DMARC) protocols to authenticate email and Work together to prevent email spoofing.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is a security protocol established as a standard in 2014. It works with DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) to prevent malware and phishing attacks.
SPF can detect spoofed emails, and it has become common in most email services to combat phishing. But using SPF is the responsibility of the domain holder. To use SPF, a domain holder must configure a DNS TXT entry specifying all IP addresses authorized to send email on behalf of the domain.
With this DNS entry configured, recipient email servers look at the IP address when receiving a message to make sure it matches the authorized IP address of the email domain. If there is a match, the Received-SPF field displays a PASS status. If there is no match, the field displays a failed status. Recipients should review this status when receiving emails with links, attachments or written instructions.
Use a secure email provider: Choose a secure email service provider that uses advanced security measures to protect against email spoofing and phishing attacks. For example, ProtonMail is a widely known and easy-to-use secure email provider.
Educate users: Train your people to recognize and avoid spoofing attacks. Share ways to identify suspicious emails that should be reported before opening.
These are some of the most common email security solutions that organizations use to better protect themselves from email spoofing and other types of cyber attacks.